Using local AI models
Generate SQL from natural language using AI CLI Proxy or Ollama for privacy-first AI
LLMs (Large Language Models) can be used to generate code from natural language questions. Popular examples
include
GitHub Copilot
,
OpenAI's GPT-4
or Anthropic's
Claude
.
SQL Workbench supports two modes for AI-powered SQL generation, both running locally on your machine for maximum privacy:
- AI CLI Proxy - Connect to cloud AI providers (Claude, Gemini, Codex, etc.) through locally installed CLI tools
- Ollama - Run the DuckDB-NSQL model entirely offline on your machine
Option 1: AI CLI Proxy (Recommended)
The AI CLI Proxy is a lightweight local server that bridges SQL Workbench to various AI command-line tools installed on your machine.
This gives you access to powerful cloud AI models while keeping your data local - the proxy runs on your machine and only sends
the table schema and your question to the AI provider.
Supported Providers
- Claude - via the
claudeCLI - Gemini - via the
geminiCLI - Codex - via the
codexCLI - Continue - via the
cnCLI - OpenCode - via the
opencodeCLI
Setup
1. Install at least one of the supported AI CLI tools on your machine and authenticate with the provider.
2. Install and start the AI CLI Proxy from
github.com/tobilg/text-to-sql-proxy
:
# Install globally
npm install -g text-to-sql-proxy
# Or run directly with npx
npx text-to-sql-proxy
The proxy will start on
http://localhost:4000 by default.
3. In SQL Workbench, open the AI settings (wand icon in the sidebar), select AI CLI Proxy mode,
and choose your preferred provider from the dropdown.
Option 2: Ollama (Offline)
For completely offline AI generation, you can use Ollama with the DuckDB-NSQL model. This model was specifically
trained for DuckDB SQL syntax with 200k DuckDB Text-to-SQL pairs.
DuckDB-NSQL is a Text-to-SQL model created by NumberStation for MotherDuck. It's hosted on
HuggingFace
and on
Ollama
. There are also some nice blog posts worth reading:
Setup
1. Install
Ollama
on your local machine.
2. Download the DuckDB-NSQL model:
ollama pull duckdb-nsql:7b
The default model is 3.8GB. There are
smaller quantized models
available, but answer quality may be lower.
3. Start Ollama with CORS enabled for SQL Workbench:
OLLAMA_ORIGINS="https://sql-workbench.com" ollama serve
Setting the
OLLAMA_ORIGINS environment variable is necessary to
enable CORS
for the browser-based SQL Workbench.
4. In SQL Workbench, open the AI settings and select Ollama mode.
Using AI in SQL Workbench
Enable the AI feature in SQL Workbench by clicking the wand icon in the sidebar:
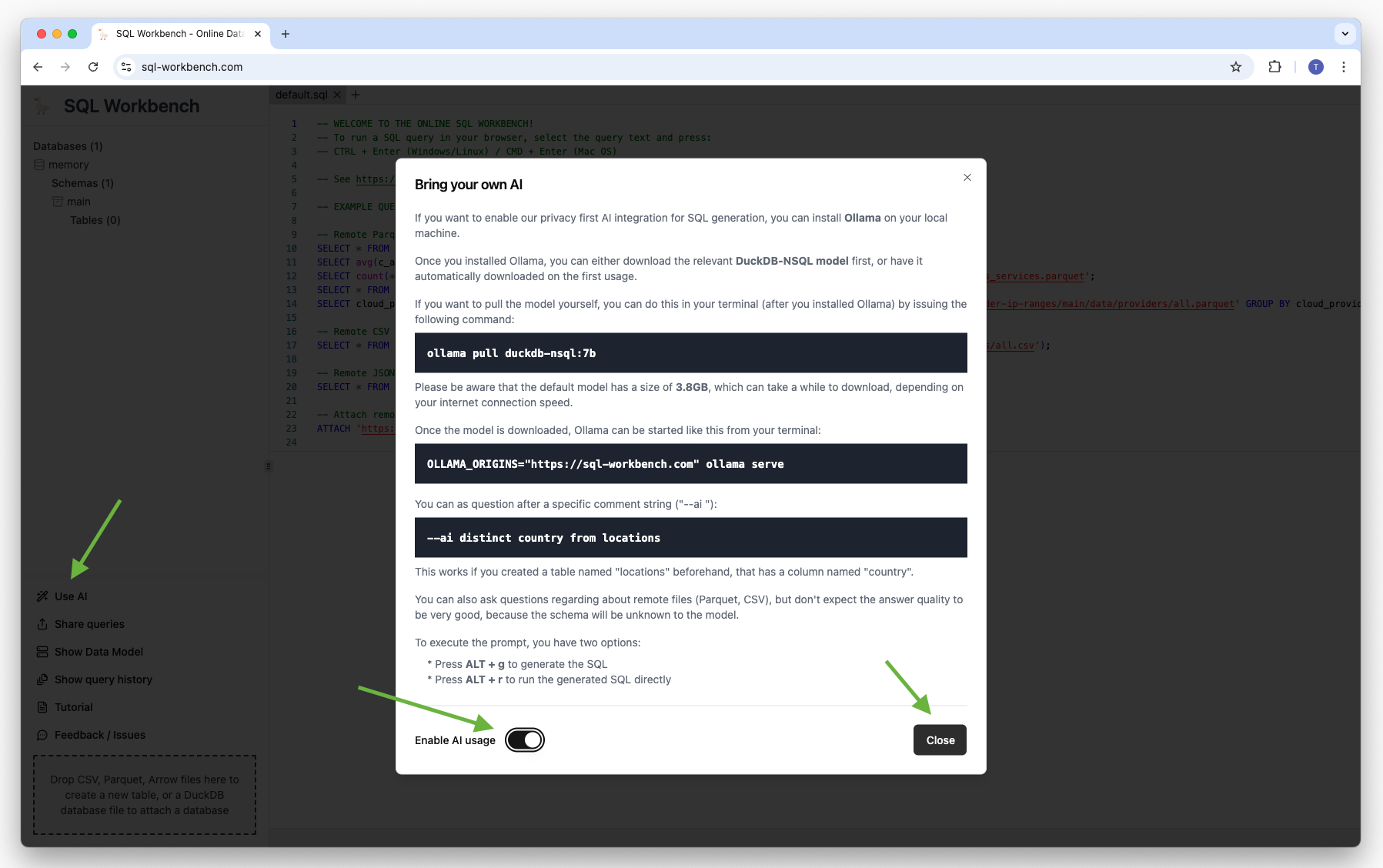
You need to create a local table first, as the AI model needs a schema to work with. For example, you can
create a table with AWS Edge Locations by using a remote dataset:
CREATE TABLE "locations" AS SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-edge-locations/main/data/aws-edge-locations.parquet';Then, you can ask your questions after a specific comment string like below:
--ai your natural language question
To execute the prompt, you have two options:
-
Press
ALT + gto generate the SQL -
Press
ALT + rto run the generated SQL directly
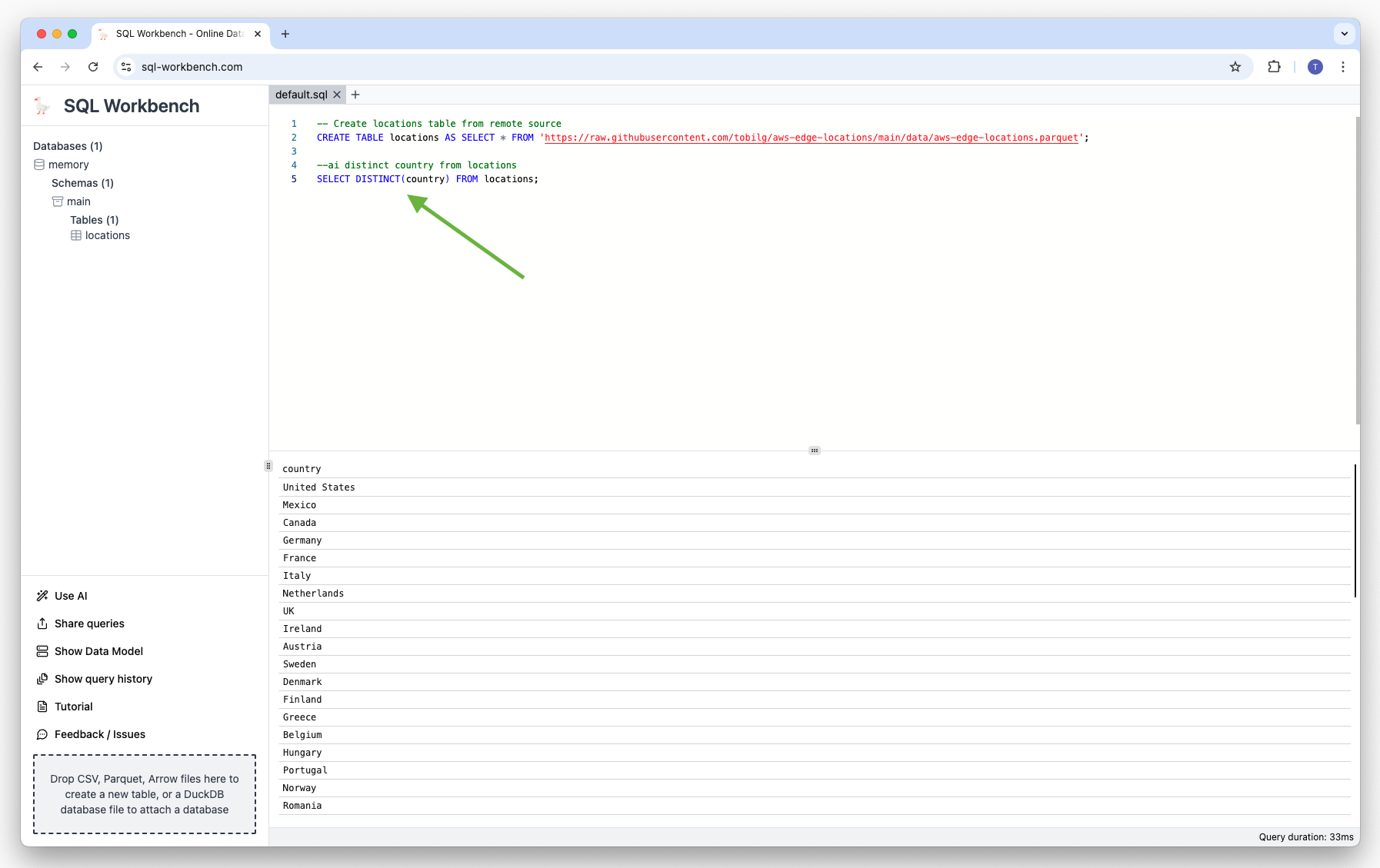
The generated SQL is automatically inserted below the closest prompt comment string. In case you have multiple
comment strings in the current SQL Workbench tab, the one closest to the actual cursor position is used.
IMPORTANT
You can also ask questions regarding about remote files (Parquet, CSV), but don't expect the answer quality
to be very good, because the schema will be unknown to the model.
The best practice would be to create a table first, and then ask questions about the data in that table.
Explore an example dataset with AI
AWS publishes its
Service Authorization Reference
documentation, and there's a
Github repository
that transforms the published data automatically to Parquet, CSV, JSON and DuckDB database formats every night
at 4AM UTC.
You first need to run the below statements to create a database structure:
CREATE TABLE services (
service_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
"name" VARCHAR,
prefix VARCHAR,
reference_url VARCHAR
);
CREATE TABLE actions (
action_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
service_id INTEGER,
"name" VARCHAR,
reference_url VARCHAR,
permission_only_flag BOOLEAN,
access_level VARCHAR,
FOREIGN KEY (service_id) REFERENCES services (service_id)
);
CREATE TABLE condition_keys (
condition_key_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
"name" VARCHAR,
reference_url VARCHAR,
description VARCHAR,
"type" VARCHAR
);
CREATE TABLE resource_types (
resource_type_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
service_id INTEGER,
"name" VARCHAR,
reference_url VARCHAR,
arn_pattern VARCHAR,
FOREIGN KEY (service_id) REFERENCES services (service_id)
);
CREATE TABLE resource_types_condition_keys (
resource_type_condition_key_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
resource_type_id INTEGER,
condition_key_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (resource_type_id) REFERENCES resource_types (resource_type_id),
FOREIGN KEY (condition_key_id) REFERENCES condition_keys (condition_key_id)
);
CREATE TABLE actions_resource_types (
action_resource_type_id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY,
action_id INTEGER,
resource_type_id INTEGER,
required_flag BOOLEAN,
FOREIGN KEY (action_id) REFERENCES actions (action_id)
);
CREATE TABLE actions_condition_keys (
action_condition_key_id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY,
action_resource_type_id BIGINT,
action_id INTEGER,
condition_key_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (action_id) REFERENCES actions (action_id),
FOREIGN KEY (condition_key_id) REFERENCES condition_keys (condition_key_id)
);
CREATE TABLE actions_dependant_actions (
action_dependent_action_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
action_resource_type_id BIGINT,
action_id INTEGER,
dependent_action_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (action_id) REFERENCES actions (action_id),
FOREIGN KEY (action_resource_type_id) REFERENCES actions_resource_types (action_resource_type_id)
);
INSERT INTO services SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_services.parquet';
INSERT INTO resource_types SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_resource_types.parquet';
INSERT INTO condition_keys SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_condition_keys.parquet';
INSERT INTO actions SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_actions.parquet';
INSERT INTO resource_types_condition_keys SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_resource_types_condition_keys.parquet';
INSERT INTO actions_resource_types SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_actions_resource_types.parquet';
INSERT INTO actions_condition_keys SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_actions_condition_keys.parquet';
INSERT INTO actions_dependant_actions SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tobilg/aws-iam-data/main/data/parquet/aws_actions_dependant_actions.parquet';
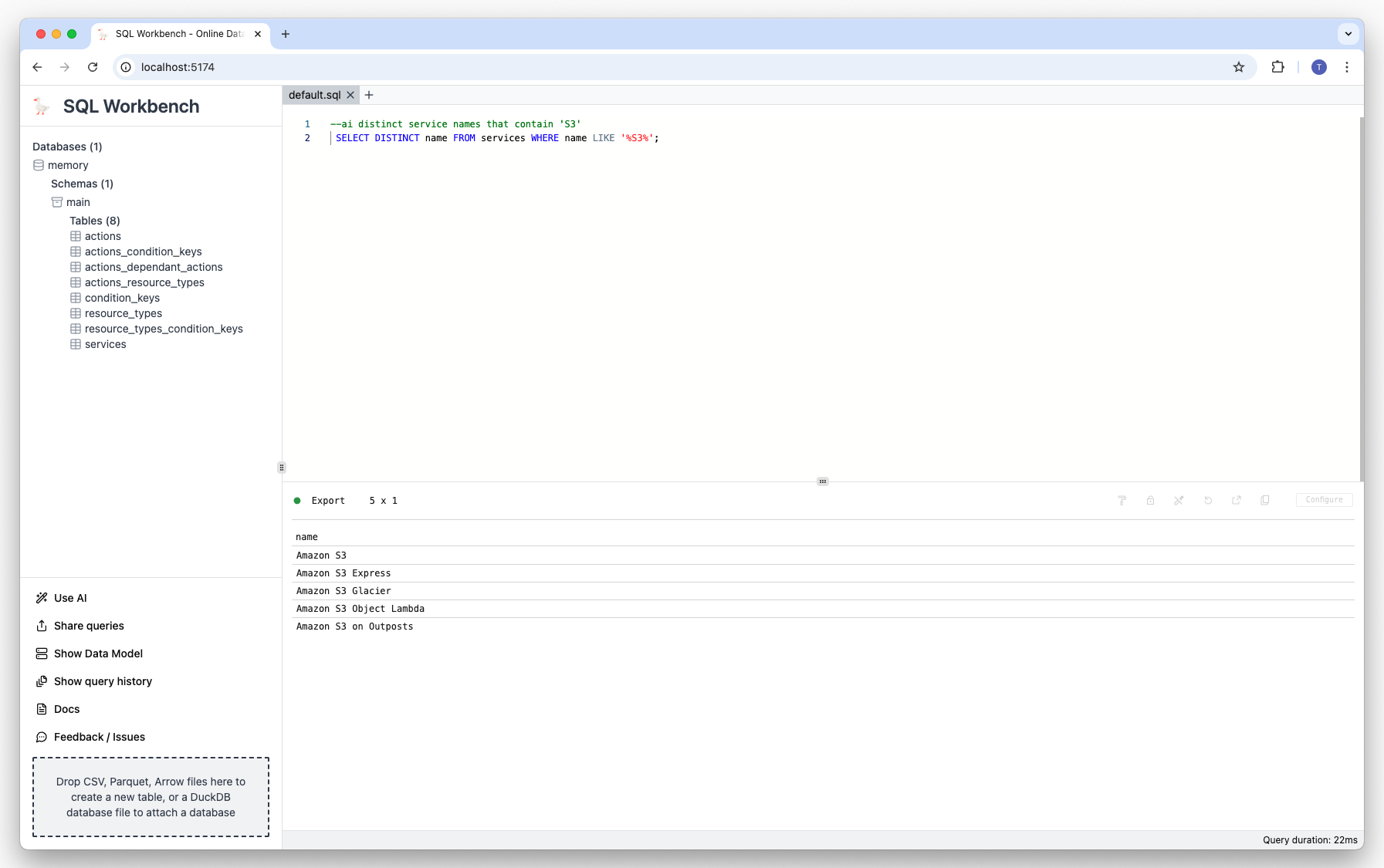
You can then explore the data with the DuckDB-NSQL model. For example, you can ask the model to show all
services that contain 'S3' in their name:
--ai distinct service names that contain 'S3'The model will generate an appropriate SQL statement, and execute it:
Other prompt examples
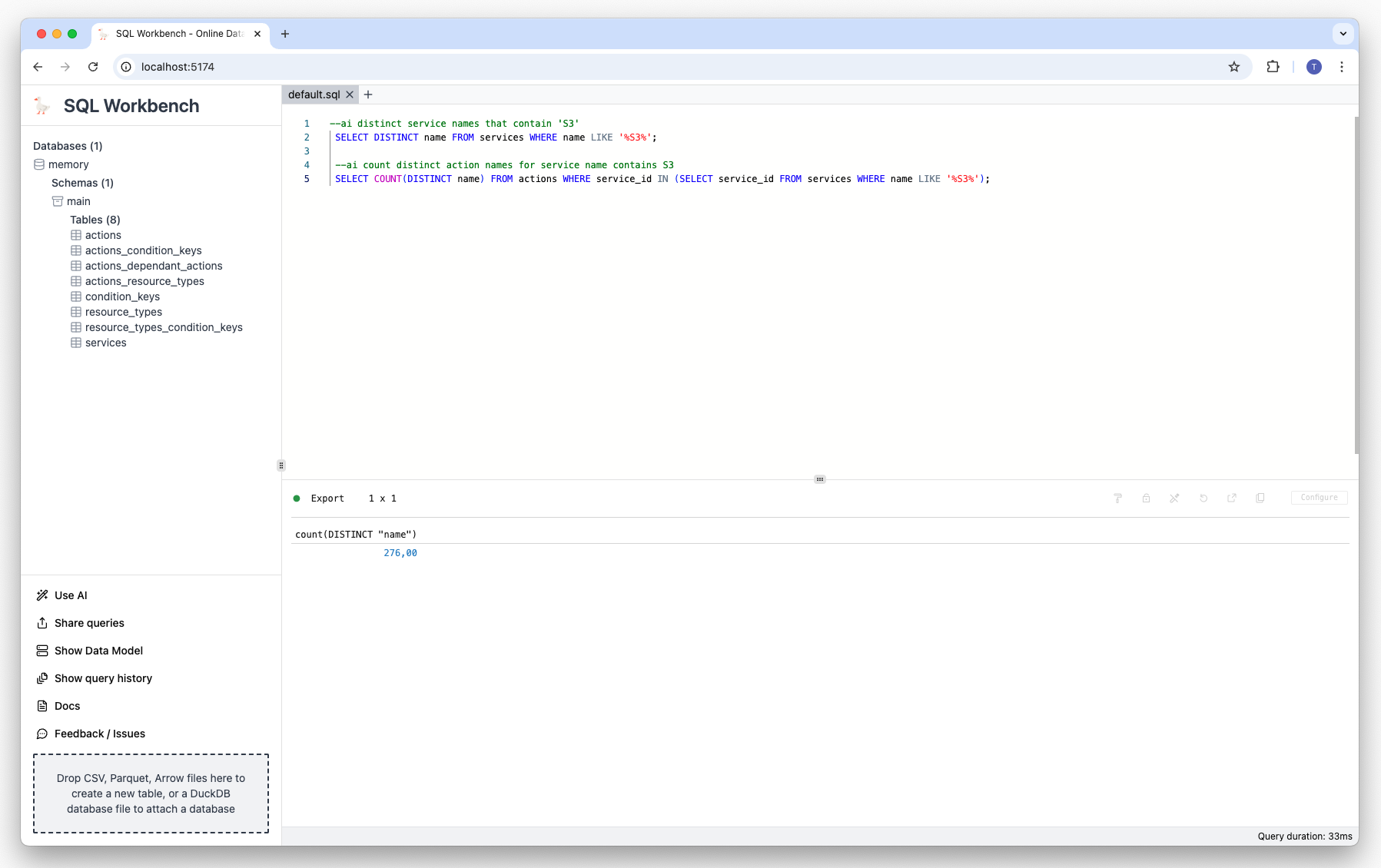
Prompt: Count the action names of services whose name contains 'S3':
--ai count distinct action names for service name contains S3 Result:
Prompt: Show all 'Write' access level actions for service 'Amazon S3':
--ai show all 'Write' access level action for service 'Amazon S3' Result:
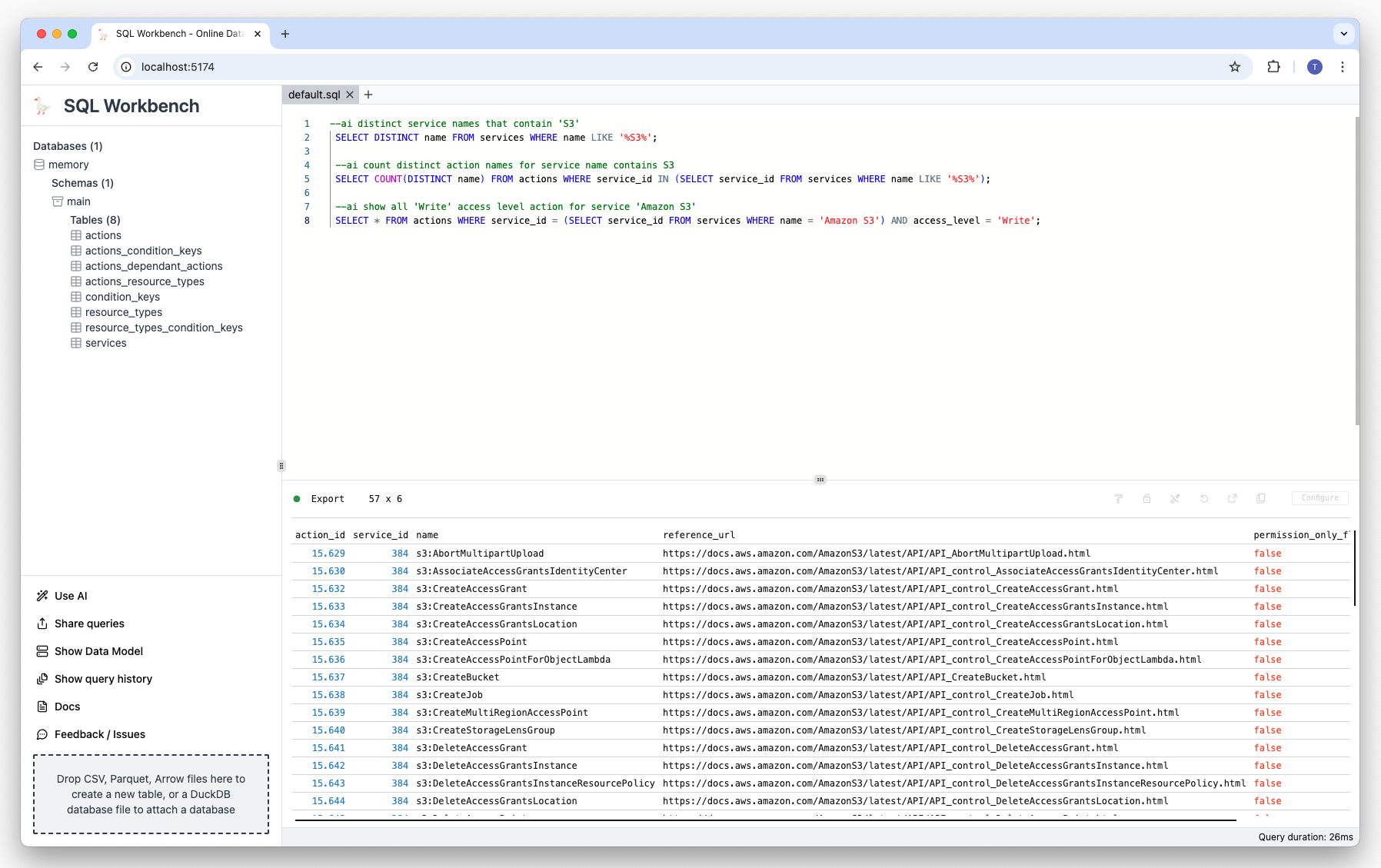
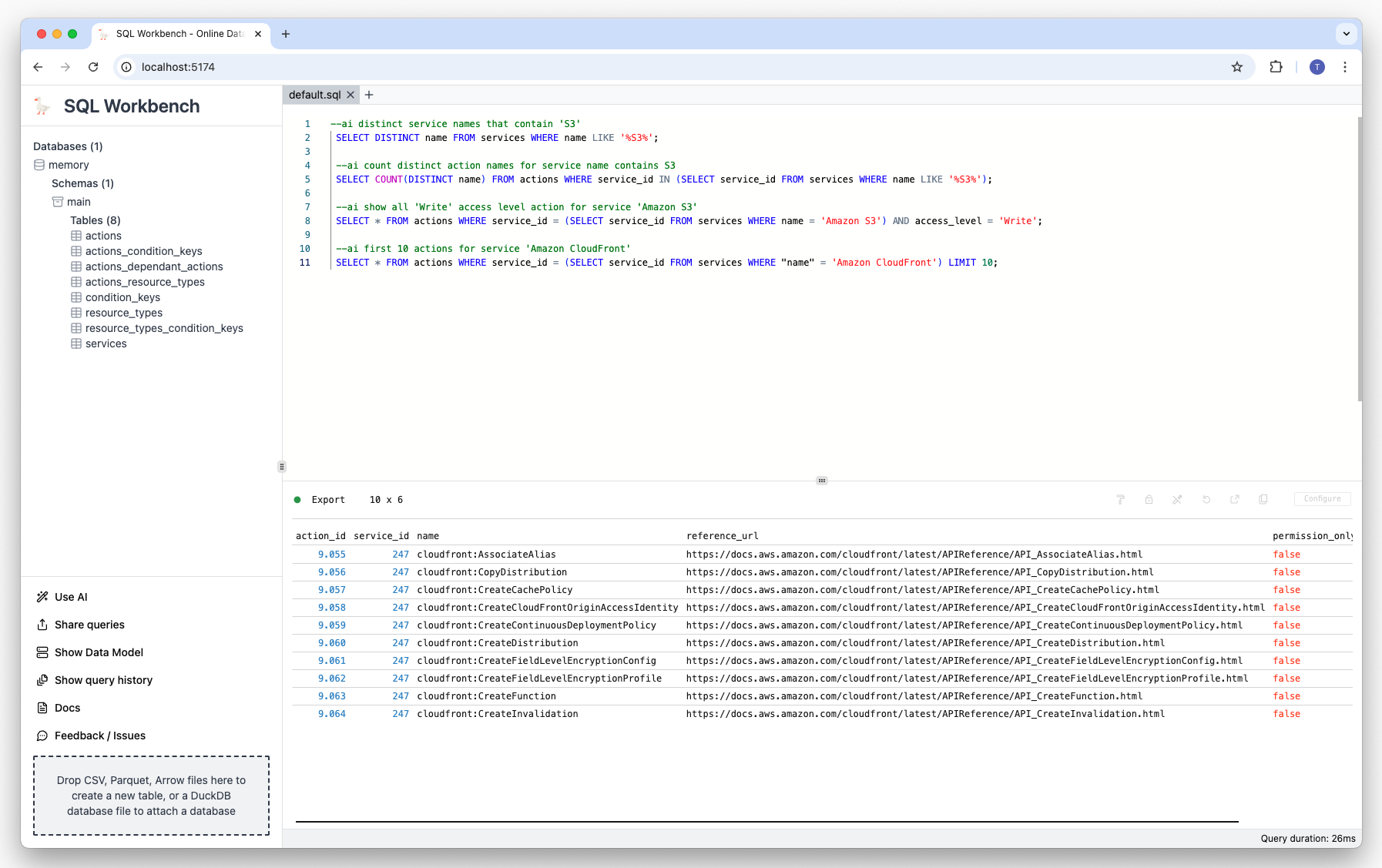
Prompt: Show first 10 actions for service 'Amazon CloudFront':
--ai first 10 actions for service 'Amazon CloudFront' Result:
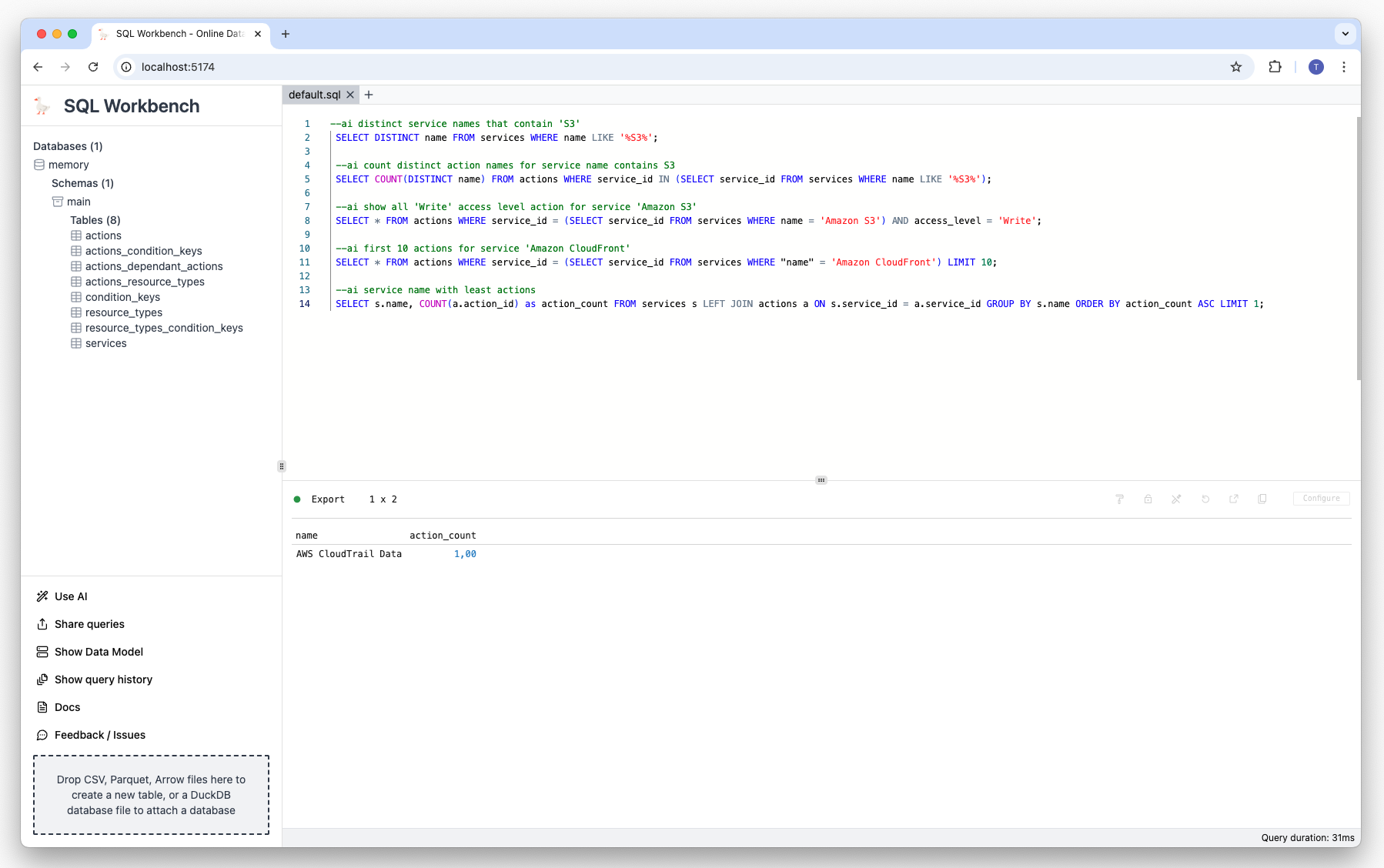
Prompt: Show service name with least actions:
--ai service name with least actions Result:
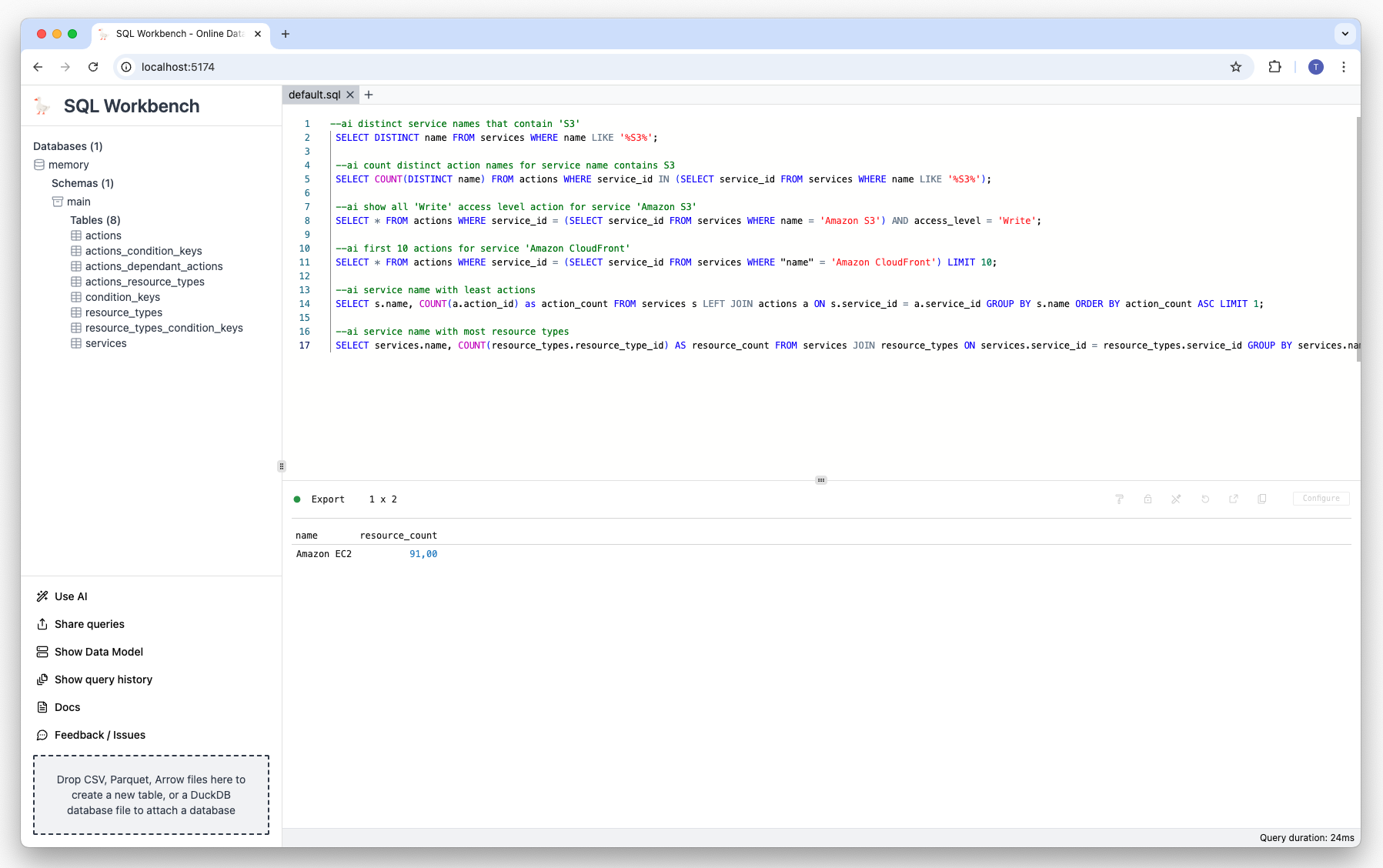
Prompt: Show service with most resource types:
--ai service name with most resource types Result:
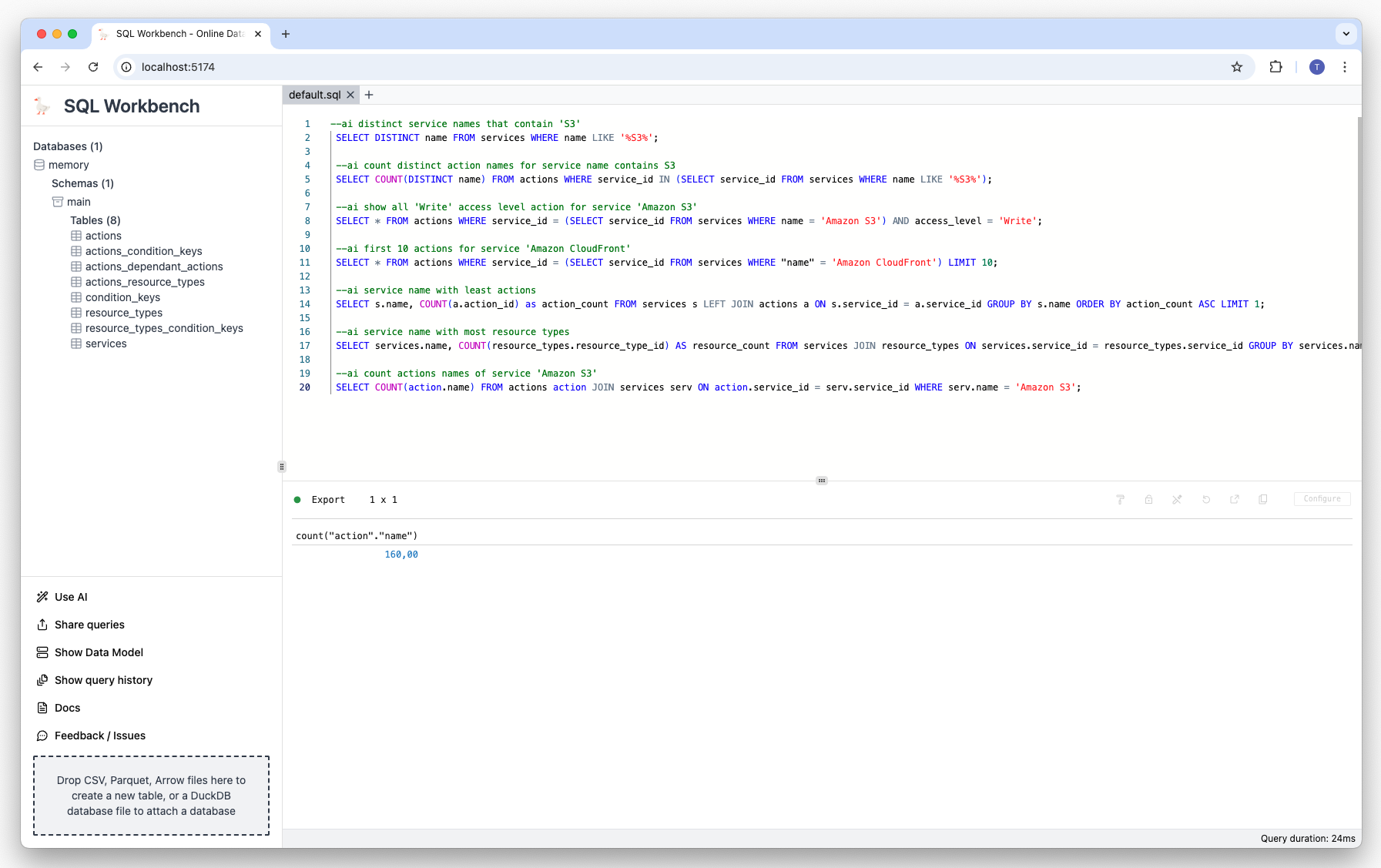
Prompt: Show the count of actions of service 'Amazon S3':
--ai count actions names of service 'Amazon S3' Result:
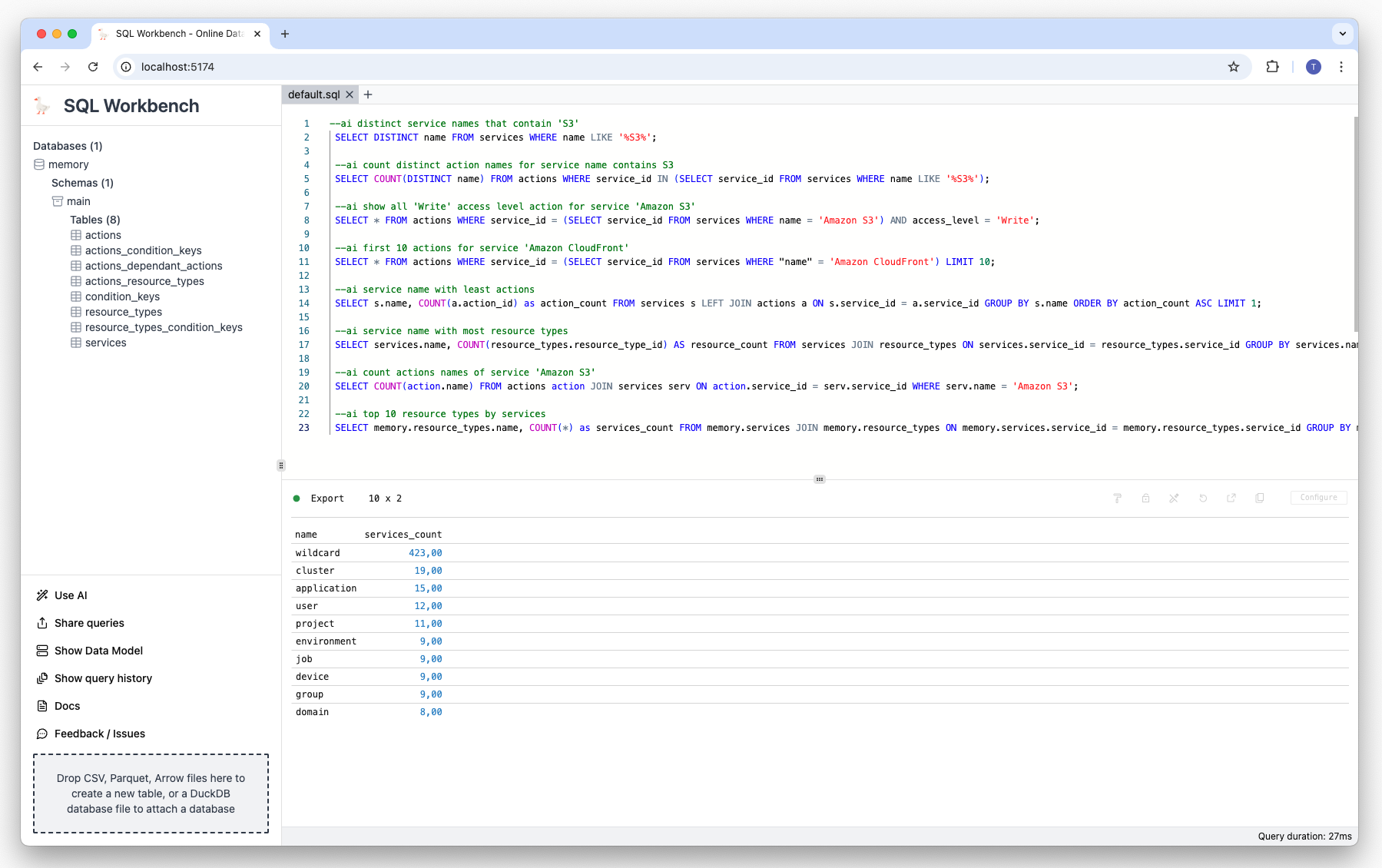
Prompt: Show the top 10 resource types by service:
--ai top 10 resource types by services Result:
Summary
Using locally running AI tools together with an in-browser SQL Workspace enables a cost-effective and
privacy-friendly way to use state of the art AI models without needing to rely on third party services
handling your data.
Demo video
There's a
demo video
on YouTube that showcases the AI features of SQL Workbench.